Learn the ins and outs of the offside in football. Our comprehensive guide explains what offside is, its history, and its importance in the beautiful game.
Table of Contents
1. Offside in football
Football is a dynamic and fast-paced sport. One of the key elements that adds intrigue to the game is the offside rule. Understanding this rule is crucial for both players and spectators. While the concept of offside might seem confusing at first, breaking it down into its components can make it more manageable to comprehend.
2. The Basics of Offside
2.1 Definition
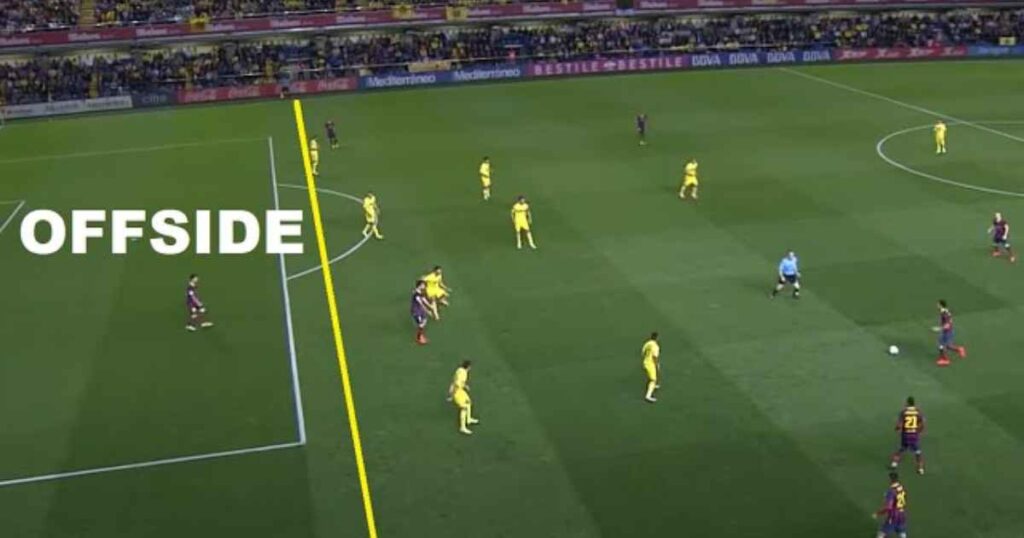
In football, the offside rule is designed to ensure fair play and prevent goal-hanging, which is when an attacking player positions themselves close to the opponent’s goal in anticipation of receiving a pass and scoring. The offside rule essentially states that a player is in an offside position if:
- They are nearer to the opponent’s goal line than both the ball and the second-to-last defender (usually the last outfield player) when the ball is played to them, unless:
- They are level with the second-to-last defender when the ball is played to them.
- They are level with the ball when it is played to them.
In simpler terms, a player is considered offside if they are closer to the opponent’s goal line than the ball and the second-to-last defender when the ball is played to them. However, being level with the second-to-last defender or the ball when the pass is made is not considered offside.
2.2 Offside Position
Being in an “offside position” is not an offense in itself. It’s only when a player in an offside position becomes actively involved in the play that an infringement occurs. To be deemed in an offside position, a player needs to be closer to the opponent’s goal line than the ball and the second-to-last defender at the moment the ball is played to them.
2.3 Involvement in Play
A player in an offside position can only be penalized for being offside if they become actively involved in the play. This involvement includes:
- Gaining an advantage from being in an offside position. For example, receiving the ball from a rebound, a deflection, or a deliberate save by an opponent.
- Interfering with an opponent. This could mean blocking the opponent’s line of vision or making a play on the ball.
If a player is in an offside position but is not involved in the play, they will not be penalized. The player must become actively involved to trigger the offside rule.
3. The History of the Offside Rule
Understanding the origins and historical development of the offside rule can provide insight into why it is an integral part of modern football.
3.1 Early Origins
The offside rule dates back to the early days of football, with variations of it being used in different forms of the sport. In the 19th century, when football was rapidly evolving and regional codes were prevalent, the offside rule was a point of contention.
In 1863, the Laws of the Game were established by the newly formed Football Association in England. This marked a significant step toward standardizing the rules of football. The original offside rule stated that a player was offside if they were positioned in front of the ball when it was played to them. This rule led to situations where players would position themselves right next to the opponent’s goal, waiting for a pass, causing significant disruptions in the flow of the game.
3.2 Evolution of the Rule
To address the issues with the offside rule, several modifications were made over the years. One notable change was introduced in 1925 when the offside law was revised to consider a player level with the second-to-last defender as not being offside. This change aimed to create a fairer balance between attacking and defensive play.
In 1990, FIFA introduced the concept of “passive offside” to further clarify the rule. A player in an offside position who was not involved in the play was no longer penalized. This clarification aimed to reduce the frequency of offside decisions and encourage continuous gameplay.

4. Offside in Action
To illustrate how the offside rule works in practice, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario on the football field. In this scenario, we have Team A, which is attacking, and Team B, which is defending.
- Team A is launching an attack, and Player X is positioned near Team B’s goal line.
- The ball is played by Player Y from Team A toward Player X.
- At the moment the ball is played, Player X is closer to the opponent’s goal line than both the ball and the second-to-last defender from Team B.
- Player X receives the ball and scores a goal.
In this scenario, Player X would be deemed offside and the goal would be disallowed. The offside rule prevents players from positioning themselves too close to the opponent’s goal line and gaining an unfair advantage.
5. Common Misconceptions
Misunderstanding or misinterpreting the offside rule is not uncommon, and there are several common misconceptions associated with it. Here are a few of the most prevalent misconceptions:
5.1 Being in an Offside Position is an Offense
One common misconception is that being in an offside position is itself an offense. As previously explained, this is not the case. To commit an offside offense, a player in an offside position must become actively involved in the play.
5.2 Timing the Run
Many fans believe that a player’s timing of their run or movement determines whether they are offside. In reality, the offside position is determined when the ball is played, not when the player starts their run. Players can time their runs to stay level with the last defender when the pass is made.
5.3 Ball-Playing Defender
Another misconception is that if a defender intentionally plays the ball, it nullifies the offside offense. This is not true. If a player in an offside position receives the ball after it rebounds off a defender or a save, they are still offside.
6. The Importance of the Offside Rule
The offside rule is essential for the balance and fairness of the game. It serves several crucial purposes in football:
6.1 Promoting Fair Play
The offside rule prevents players from lurking near the opponent’s goal line, waiting for an easy goal. Without this rule, the attacking team could continuously exploit this tactic, making the game less competitive and entertaining.
6.2 Encouraging Defensive Skills
The rule forces defending teams to stay organized and maintain a solid defensive line. This promotes the development of defensive skills, team coordination, and tactical strategies.
6.3 Aiding Game Flow
By preventing offside positions and offenses, the offside rule helps maintain the flow of the game. It minimizes interruptions, allowing for a more dynamic and exciting match.
6.4 Fostering Sportsmanship
The offside rule encourages players to compete fairly and within the established rules of the game. This fosters sportsmanship and a sense of fair play on the field.

Some lesser-known facts about the offside rule in football:
- No Offside in Own Half: A player cannot be offside when receiving the ball directly from a goal kick, corner kick, or throw-in. So, if a player is in their own half when the ball is played to them, they are not considered offside.
- Not Offside from Goal Kicks: Similarly, a player cannot be offside from a goal kick. So, if the goalkeeper plays the ball to a teammate directly from a goal kick, they are not in an offside position.
- Not Offside from Throw-Ins: When a player receives the ball directly from a throw-in, they are not considered offside, regardless of their position on the field.
- The Ball or the Second-to-Last Defender: A player is considered offside if they are nearer to the opponent’s goal line than both the ball and the second-to-last defender (usually the last outfield player) when the ball is played to them.
- Not Offside in Own Half at the Moment of Release: It’s essential to note that a player is only considered offside if they are in the opponent’s half at the moment the ball is played to them by a teammate.
- Active Involvement: To be penalized for being offside, a player must also be actively involved in the play. This includes interfering with an opponent or gaining an advantage from being in an offside position.
- Offside Offenses in the Build-Up: Sometimes, goals are disallowed due to an offside position during the build-up to the goal-scoring opportunity, even if the player in the offside position did not touch the ball.
- AR (Assistant Referee) Decision: The decision on offside is often challenging for referees to make in real-time. Assistant referees play a crucial role in signaling offside based on their position along the touchline.
- VAR (Video Assistant Referee): VAR has been introduced to assist with more accurate decisions, including offside calls. This has led to more precise but sometimes contentious decisions, as VAR can scrutinize the position of players down to centimeters.
- Subjectivity in Offside Calls: Despite attempts to make offside decisions more objective, there is still an element of subjectivity, especially in interpreting whether a player is “interfering with an opponent” or “gaining an advantage.”
Some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to the offside rule in football, along with their answers:
Q1: What is the offside rule in football?
A1: The offside rule in football is designed to prevent unfair play and to maintain the integrity and balance of the game. It states that a player is in an offside position if they are closer to the opponent’s goal line than both the ball and the second-to-last defender (usually the last outfield player) when the ball is played to them. However, being level with the second-to-last defender or the ball when the pass is made is not considered offside.
Q2: Is being in an offside position itself an offense?
A2: No, being in an offside position is not an offense in itself. To commit an offside offense, a player in an offside position must become actively involved in the play. This involvement can include gaining an advantage from their position or interfering with an opponent.
Q3: Does a player need to be in line with the last defender to avoid being offside?
A3: No, a player doesn’t need to be in line with the last defender to avoid being offside. To be onside, a player must be level with the second-to-last defender or the ball when it is played to them. Being level with the last defender is not required to avoid offside.
Q4: Can a player time their run to stay onside?
A4: Yes, players often time their runs to stay onside. The key factor in determining offside is the player’s position concerning the second-to-last defender and the ball when the pass is made. Players can start their runs to ensure they are level with the second-to-last defender or the ball at that moment.
Q5: What happens when a player is offside?
A5: When a player is offside and becomes actively involved in the play, the opposing team is awarded an indirect free-kick from the spot where the offside player interfered with play. If a player scores while in an offside position, the goal is disallowed.
Q6: Can a defender intentionally play the ball to nullify an offside offense?
A6: No, if a defender intentionally plays the ball and it deflects to an offside player, the offside offense is not nullified. The offside player is still considered offside because the original intent of the offside rule is to prevent players from taking advantage of their position near the opponent’s goal line.
Q7: What is the purpose of the offside rule in football?
A7: The offside rule serves several essential purposes, including promoting fair play, encouraging defensive skills, aiding game flow, and fostering sportsmanship. It prevents goal-hanging, maintains balance between attacking and defensive play, and ensures a more dynamic and exciting game.
Q8: Are there any exceptions to the offside rule?
A8: There are a few exceptions to the offside rule, such as when a player receives the ball directly from a goal kick, corner kick, or throw-in. In these cases, the player cannot be offside. Additionally, a player cannot be offside in their own half of the field.
Q9: How has the offside rule evolved over time?
A9: The offside rule has undergone several changes throughout its history. Notably, in 1925, the law was amended to allow players to be level with the second-to-last defender and not be considered offside. In 1990, the concept of “passive offside” was introduced, meaning that a player in an offside position who is not involved in the play is not penalized.
Q10: Why is understanding the offside rule important for fans and players?
A10: Understanding the offside rule is crucial for fans and players because it enhances the enjoyment and integrity of the game. It allows spectators to follow the action and appreciate the tactical aspects of football. For players, knowing the rule is essential to avoid committing offside offenses and to strategically position themselves during a match.
Must read this articles👇👇
Originally posted 2023-10-19 21:45:58.




1 Comment